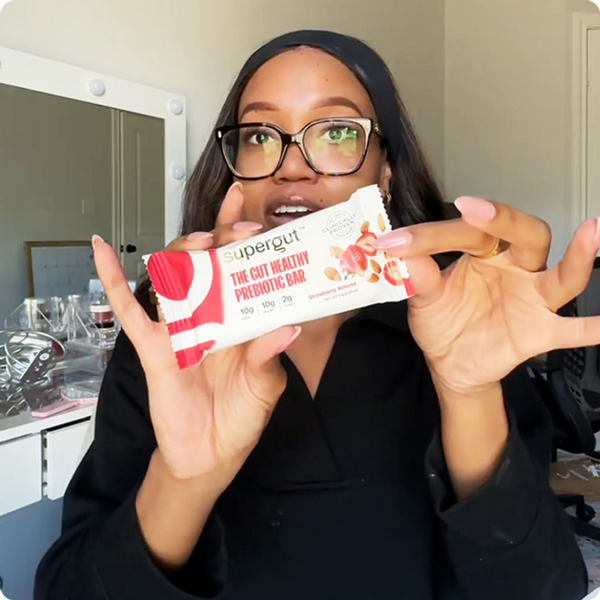
Daily Gut Health Done Better
THE SECRET TO GUT HEALTH
30g Daily.
It's That Simple.
The simple upgrade to improving gut health, and all that comes with it, is getting your daily dose of prebiotic fiber.
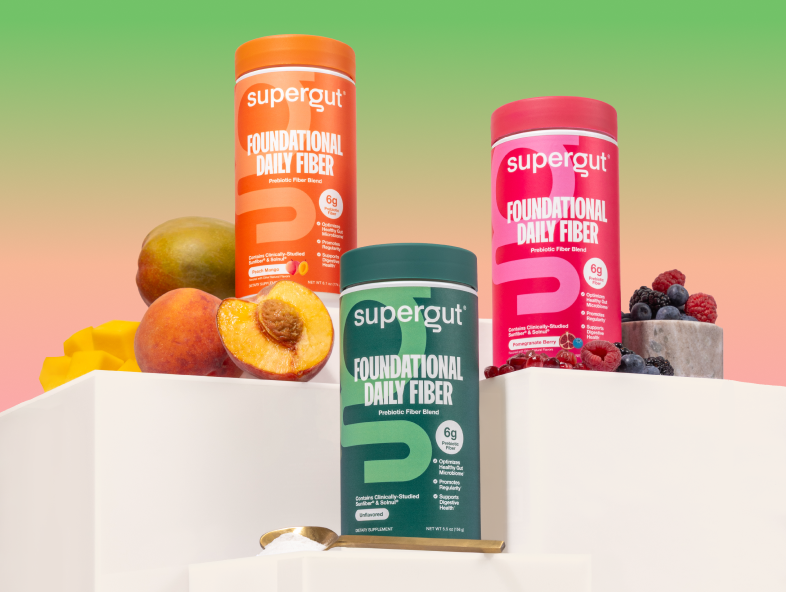
Foundational Daily Fiber Blend
Your daily gut health essential


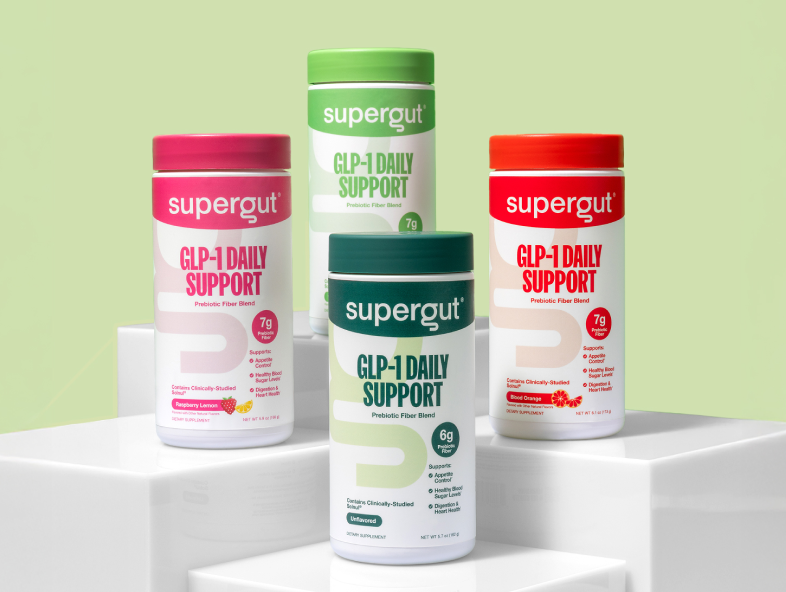
GLP-1 Daily Support Fiber Blend
Gut health + metabolic support
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
^When taken with a meal, this product may help support feelings of fullness, reduce occasional cravings and increase beneficial gut bacteria associated with natural GLP-1 production. Results may vary.
Not Just Any Fiber
Powered by the most premium prebiotic sources, our clinically-backed blends of soluble + insoluble fiber nourish your microbiome with greater efficacy & without the digestive discomfort.
-
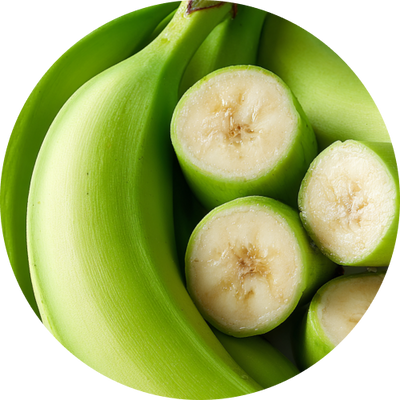 Unripened Green BananaFosters a diverse microbiome to aid immunity, skin, & brain health.
Unripened Green BananaFosters a diverse microbiome to aid immunity, skin, & brain health. -
 Solnul® Resistant Potato StarchOptimizes healthy microbial balance and supports metabolic health*.
Solnul® Resistant Potato StarchOptimizes healthy microbial balance and supports metabolic health*. -
 Sunfiber®Guar FiberSupports regularity and digestion without gas, bloating, or discomfort.*
Sunfiber®Guar FiberSupports regularity and digestion without gas, bloating, or discomfort.* -
 Oat Beta GlucanSupports natural GLP-1 production, appetite control, & weight loss*.
Oat Beta GlucanSupports natural GLP-1 production, appetite control, & weight loss*. -
 Soluble Vegetable FiberHelps with digestion, bloating, consistency, and regularity*.
Soluble Vegetable FiberHelps with digestion, bloating, consistency, and regularity*.
Solnul® is a registered trademark of MSP Starch Products Inc. Sunfiber® is a registered trademark of Taiyo International, Inc.
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
How Supergut Works
With daily use, Supergut nourishes gut microbes to deliver measurable metabolic health results.
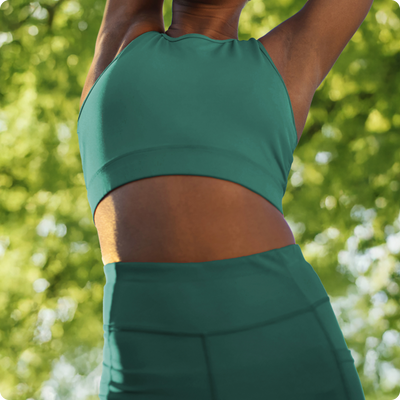

Microbiome Who?
Your gut is home to trillions of microbes that impact everything from digestion to appetite. Feed them right, and they'll return the favor.
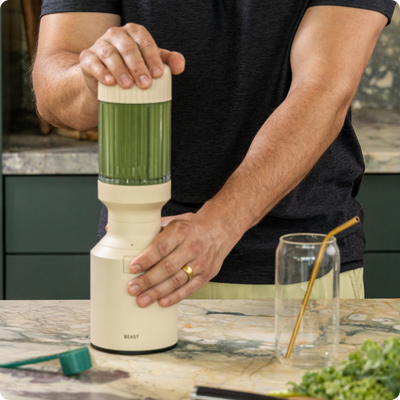

Take Daily Why?
95% of Americans are fiber deficient & 93% metabolically unhealthy. Daily use helps flip the script of being "overfed yet undernourished."

So... Which?
Different goals call for different tools. Foundational Fiber is your daily gut health essential. GLP-1 Daily Support supports your gut plus metabolic health*.
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
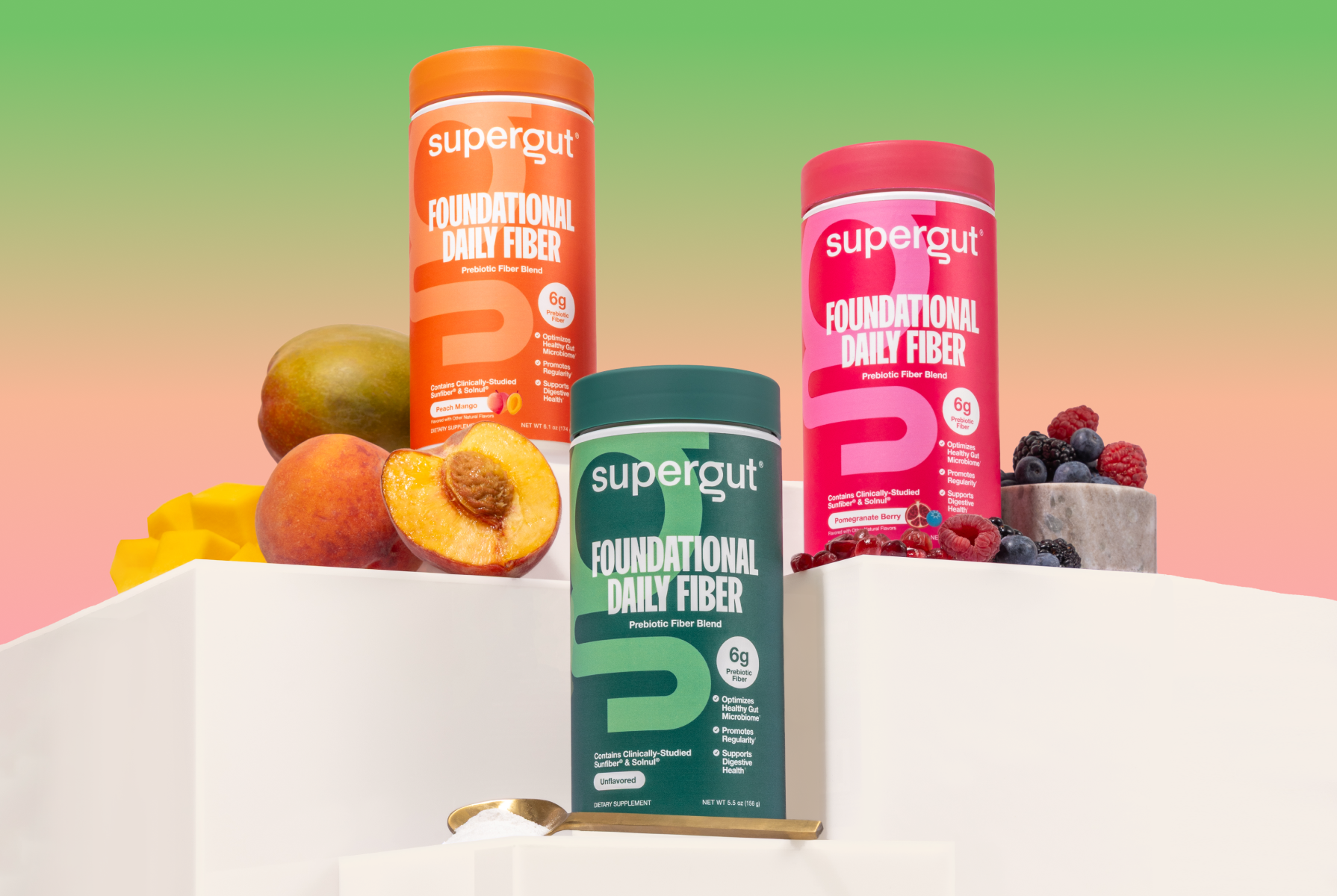






![[Variety Pack] [On-The-Go Packets (15 Servings)]](http://supergut.com/cdn/shop/files/FDF_Main_Product_Image.png?v=1772476823&width=750)
![[Unflavored] [20 Servings]](http://supergut.com/cdn/shop/files/02_-_Stylized_Product_-_Unflavored_-_Canister_4bbfdaf1-636e-449a-9366-fc2da20fa676.png?v=1772476823&width=750)





















